Polymers have a wide range of applications, from product packaging and textiles to construction and industrial machinery, among others. The material properties of polymers are closely related to their relative molecular weight, which is an indispensable parameter in polymer research and production quality control.
The viscosity method is currently the most commonly used relative method for determining the relative molecular weight of polymers. There are usually four methods for measuring liquid viscosity: capillary method, falling ball method, rotational viscosity method, and pressure method. In chemical fiber and plastic laboratories, capillary method is generally used.
Relative viscosity (viscosity ratio): The ratio of the viscosity of a solution to the viscosity of a solvent at the same temperature.
Incremental viscosity (relative increase in viscosity): The ratio of the difference between the viscosity of a solution and the viscosity of a solvent to the viscosity of the solvent.
Viscosity (specific viscosity): For polymer solutions, viscosity often increases with the increase of solution concentration, and its specific viscosity also increases with the increase of solution concentration. Therefore, the ratio of viscosity to concentration is commonly used to represent the viscosity of the solution, which is called viscosity number.
Logarithmic viscosity: The ratio of the natural logarithm of relative viscosity to concentration.
Intrinsic viscosity (ultimate viscosity): refers to the limit value of the viscosity or logarithmic viscosity of a polymer solution at infinite dilution.
The intrinsic viscosity of polymers is determined by capillary method to characterize their relative molecular weight.
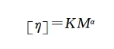
In polymer testing, different solvents need to be prepared according to the properties of the polymer. Many of these solvents have strong odors and even toxicity, such as phenol o-dichlorobenzene. Therefore, using an automatic polymer viscosity tester can not only improve testing efficiency but also protect the safety of testers.
The CANNON miniPV series fully automatic polymer dilute solution kinematic viscosity tester can accurately and quickly measure the viscosity of polymer dilute solutions, calculate relative viscosity, intrinsic viscosity, specific viscosity, and intrinsic viscosity, and comply with ASTM D2857, ISO 1628, ASTM D1243, D1795, D4243, GB/T 1632, GB/T 3401, GT/T 12006, USP 911, PAPTAC G.24P, etc.
The miniPV series adopts an improved Ubbelohde viscosity tube with a standard viscosity range of 0.02~700cSt. If you have a wider range of needs, CANNON also provides customized services to meet your needs. The highly integrated miniPV adopts Peltier refrigeration technology, which expands the detection range to 15-100 ℃ without the need for external refrigeration equipment, while ensuring high-precision temperature control with a deviation of only ± 0.01 ℃. MiniPV offers two sensor options, thermal and optical, which can be appropriately matched according to usage to accurately complete testing, allowing the use of viscosity meters to be unrestricted by materials. MiniPV is suitable for solvents such as elastomers, plastics, TPE, copolymers, biopolymers, oligomers, prepolymers, resins, and viscosity improvers, and is suitable for most polymer solvents. Compact in size, it can be easily placed in a fume hood to reduce the escape of harmful gases. It is also equipped with a 10 position automatic sampler to improve testing efficiency.


Sometimes polymer solvents can have a certain degree of corrosiveness, which poses a challenge to the corrosion resistance of instruments. MiniPV HX adopts new materials to meet the requirements of corrosion resistance and acid resistance of the instrument to solvents. Both miniPV HX and miniPV adopt a dual solvent cleaning system and a compressed air drying system to ensure the cleanliness of the instrument and shorten the cleaning time.
CANNON's PolyVISA fully automatic polymer dilute solution viscosity analyzer has stronger corrosion resistance, including concentrated acid, and the temperature range can be extended up to 20-135 ℃. In addition, PolyVISA uses unique air bath technology to quickly change the target temperature and achieve temperature equilibrium. PolyVISA also has a wider viscosity range (compared to standard miniPV): 0.3~60000cSt, which is compatible with measuring polymer viscosity and oil viscosity. PolyVISA has an 11 bit automatic sampling tray that can quickly complete detection and is easy to operate.
PolyVISA uses a built-in cavity to minimize the escape of harmful gases to the greatest extent possible. PolyVISA can be used to test polymer solutions with low solubility. While equipped with a temperature measurement of 135 ℃, PolyVISA also adds an insulation system during the waste liquid discharge process to ensure that the polymer solution can be completely discharged from the system after testing, ensuring smooth experiments.

CANNON polymer viscosity tester provides you with a more environmentally friendly, faster, and more convenient polymer viscosity test!